SQLBolt 课程学习笔记一 (1-5 课)
文章目录
终究还是要回来好好补课,看文档太无聊。看网上很多人都推荐 SQLBolt 这个在线网站学习课程,所以今天就打算来看这个了。

整个课程包括介绍 + 18 节课 + 结束课程。网站不需要注册,每节课包括简单地知识点介绍和练习题。做练习题时有实时命令错误提示和结果预览,只有答对才能继续下一题。实在不会做也有 Solution 放在旁边,非常好。
好的,开始吧。
Introduction to SQL
Welcome to SQLBolt, a series of interactive lessons and exercises designed to help you quickly learn SQL right in your browser.
在浏览器里学习 SQL,好。
SQL, or Structured Query Language, is a language designed to allow both technical and non-technical users query, manipulate, and transform data from a relational database. And due to its simplicity, SQL databases provide safe and scalable storage for millions of websites and mobile applications.
才知道 SQL 是 Structured Query Language 的缩写,好吧。
Since most users will be learning SQL to interact with an existing database, the lessons begin by introducing you to the various parts of an SQL query. The later lessons will then show you how to alter a table (or schema) and create new tables from scratch.
课程首先教我们怎么查询既有数据库,后面再教怎么创建和修改数据库、表格和 Schema。
By the end, we hope you will be able to have a strong foundation for using SQL in your own projects and beyond.
好的,开始上课吧。
SQL Lesson 1: SELECT queries 101
第一节课学取数据,语法就很简单咯:
|
|
练习题是一个关于电影数据的表格:
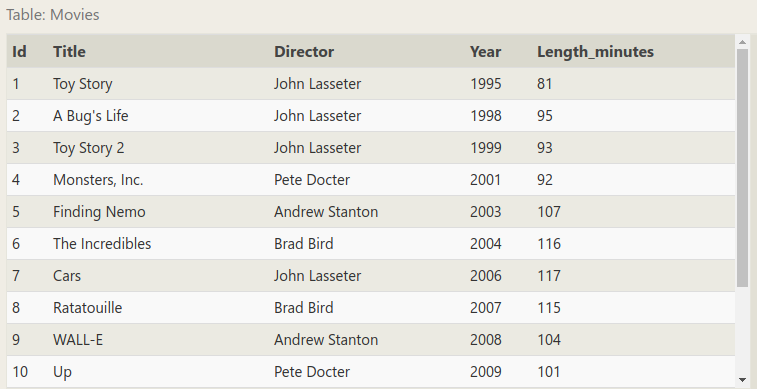
来看题目:
1. Find the title of each film
简单:
|
|
2. Find the director of each film
一样,
|
|
3. Find the title and director of each film
1 + 2 咯:
|
|
4. Find the title and year of each film
和 3 差不多:
|
|
5. Find all the information about each film
全部,
|
|
(列表嵌套代码似乎 markdown 渲染有问题,只能把问题全部加粗才能正常渲染,不然题目其实是不需要全部加粗的)
第一课轻松收工,撒花。
SQL Lesson 2: Queries with constraints (Pt. 1)
第二课主要是学习带限制性语句的查询。
Now we know how to select for specific columns of data from a table, but if you had a table with a hundred million rows of data, reading through all the rows would be inefficient and perhaps even impossible.
第一节课学习的是怎么查询表的特定列。但是当一个表极其大,有 N 多行的时候,我们可能只想得到某些特定的行,这时候就要用限制性查询语句了。
In order to filter certain results from being returned, we need to use a WHERE clause in the query. The clause is applied to each row of data by checking specific column values to determine whether it should be included in the results or not.
限制性查询通过 WHERE 从句实现,它会在数据的每一行执行判断来决定结果应该包含哪些行。基本语法为:
|
|
More complex clauses can be constructed by joining numerous AND or OR logical keywords.
复杂的限制条件可以通过使用 AND 或者 OR 组成。以及还有其他一些:
| Operator | Condition | SQL Example |
|---|---|---|
| =, !=, < <=, >, >= | Standard numerical operators | col_name != 4 |
| BETWEEN … AND … | Number is within range of two values (inclusive) | col_name BETWEEN 1.5 AND 10.5 |
| NOT BETWEEN … AND … | Number is not within range of two values (inclusive) | col_name NOT BETWEEN 1 AND 10 |
| IN (…) | Number exists in a list | col_name IN (2, 4, 6) |
| NOT IN (…) | Number does not exist in a list | col_name NOT IN (1, 3, 5) |
As you might have noticed by now, SQL doesn’t require you to write the keywords all capitalized, but as a convention, it helps people distinguish SQL keywords from column and tables names, and makes the query easier to read.
SQL 不要求命令大写,但是习惯上大家为了可读性都惯例性的把命令大写。好的,当然。
又到了紧张刺激的练习题时间。
表格还是那张表格:
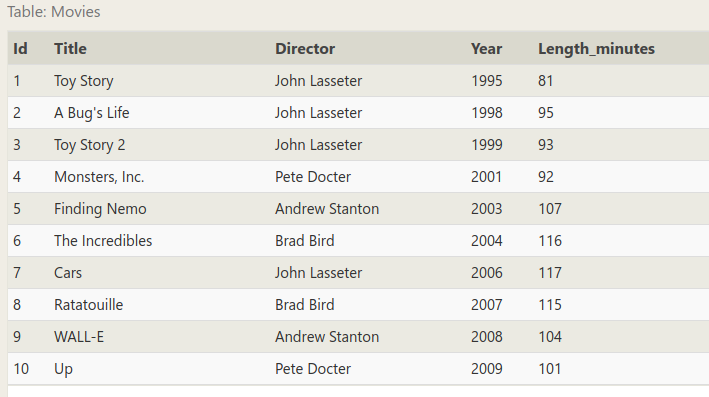
1. Find the movie with a row id of 6
row id 是 6 的电影,简单,
|
|
2. Find the movies released in the years between 2000 and 2010
BETWEEN 嘛,好说,
|
|
3. Find the movies not released in the years between 2000 and 2010
NOT BETWEEN 嘛,也好说,
|
|
4. Find the first 5 Pixar movies and their release year
前 5 个,LIMIT 超纲了啊老师,
|
|
学完走人
SQL Lesson 3: Queries with constraints (Pt. 2)
第三课继续学习限制性查询语句。
When writing WHERE clauses with columns containing text data, SQL supports a number of useful operators to do things like case-insensitive string comparison and wildcard pattern matching.
WHERE 从句支持大小写敏感/非敏感的字符串比较,一些例子:
| Operator | Condition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Case sensitive exact string comparison (notice the single equals) | col_name = “abc” |
| != or <> | Case sensitive exact string inequality comparison | col_name != “abcd” |
| LIKE | Case insensitive exact string comparison | col_name LIKE “ABC” |
| NOT LIKE | Case insensitive exact string inequality comparison col_name | NOT LIKE “ABCD” |
| % | Used anywhere in a string to match a sequence of zero or more characters (only with LIKE or NOT LIKE) | col_name LIKE “%AT%” (matches “AT”, “ATTIC”, “CAT” or even “BATS”) |
| _ | Used anywhere in a string to match a single character (only with LIKE or NOT LIKE) | colname LIKE “AN” (matches “AND”, but not “AN”) |
| IN (…) | String exists in a list | col_name IN (“A”, “B”, “C”) |
| NOT IN (…) | String does not exist in a list | col_name NOT IN (“D”, “E”, “F”) |
趁热打铁练习一下:
1.Find all the Toy Story movies
Toy Story 系列电影有 2、3,所以就要匹配 Toy Story* 这样的模式,SQL 用 %,即
|
|
2.Find all the movies directed by John Lasseter
John Lasseter 的电影,得用 =,保不齐有个 John Lasseter Jr. 之类的,所以等于靠谱点,
|
|
3.Find all the movies (and director) not directed by John Lasseter
|
|
4.Find all the WALL-* movies
和第 1 题很像,
|
|
NEXT –>>
SQL Lesson 4: Filtering and sorting Query results
对查询结果作筛选和排序
Even though the data in a database may be unique, the results of any particular query may not be – take our Movies table for example, many different movies can be released the same year. In such cases, SQL provides a convenient way to discard rows that have a duplicate column value by using the DISTINCT keyword.
虽然数据库里的数据每行可能都是唯一的,但是查询结果就不一定了,比如我们用的电影这个表格里有很多电影都是在相同年份发行的。这时候要取要对某列取唯一值就得用 DISTINCT 关键字了。语法:
|
|
Since the DISTINCT keyword will blindly remove duplicate rows, we will learn in a future lesson how to discard duplicates based on specific columns using grouping and the GROUP BY clause.
DISTINCT 是简单粗暴的直接移除重复行,后面我们会学习通过 GROUP BY 从句来处理重复值。
Ordering results
Unlike our neatly ordered table in the last few lessons, most data in real databases are added in no particular column order. As a result, it can be difficult to read through and understand the results of a query as the size of a table increases to thousands or even millions rows.
To help with this, SQL provides a way to sort your results by a given column in ascending or descending order using the ORDER BY clause.
现实世界的数据往往一团糟没有很好的排序,我们经常需要针对某一列排序来更好地组织结果,这就要用到 ORDER BY 从句了。语法:
|
|
When an ORDER BY clause is specified, each row is sorted alpha-numerically based on the specified column’s value. In some databases, you can also specify a collation to better sort data containing international text.
ORDER BY 是根据字母表顺序排序的。
Limiting results to a subset
Another clause which is commonly used with the ORDER BY clause are the LIMIT and OFFSET clauses, which are a useful optimization to indicate to the database the subset of the results you care about. The LIMIT will reduce the number of rows to return, and the optional OFFSET will specify where to begin counting the number rows from.
LIMIT 和 OFFSET 经常和 ORDER BY 搭配使用。前者指定取多少行,后者指定从第几行开始数。语法:
|
|
If you think about websites like Reddit or Pinterest, the front page is a list of links sorted by popularity and time, and each subsequent page can be represented by sets of links at different offsets in the database. Using these clauses, the database can then execute queries faster and more efficiently by processing and returning only the requested content.
想想 Reddit、 Pinterest 之类的网站,首页一般就是根据热度和时间排序的一堆链接(ORDER BY + LIMIT 的结果),后续页的链接就是在前面的页面基础上 OFFSET 出来的。用这些从句使得数据库查询每一次都只处理需要的结果,应而查询速度更快效率更高。
If you are curious about when the LIMIT and OFFSET are applied relative to the other parts of a query, they are generally done last after the other clauses have been applied. We’ll touch more on this in Lesson 12: Order of execution after introducting a few more parts of the query.
你可能很好奇 LIMIT 和 OFFSET 相对与整个从句的执行先后顺序,事实上它们基本上是在其他从句执行之后才执行的。后面的第 12 课会讲查询语句的执行顺序的。
一课一练时间到。
表格还是那张表格,这样子:

题目:
1. List all directors of Pixar movies (alphabetically), without duplicates
不重复的列出所有导演并排序,
|
|
2. List the last four Pixar movies released (ordered from most recent to least)
按时间从近到远列出最新的 4 部电影,
|
|
3. List the first five Pixar movies sorted alphabetically
排序后列出前 5 部电影,
|
|
4. List the next five Pixar movies sorted alphabetically
3 的基础上下 5 部,那就是 OFFSET 了,
|
|
SQL Review: Simple SELECT Queries
第五节课是复习。前面学的:
|
|
In the exercise below, you will be working with a different table. This table instead contains information about a few of the most populous cities of North America including their population and geo-spatial location in the world.
这次练习会用到跟前面不同的一张表格,这张表格是北美一些最大的城市的地理位置和人口情况:
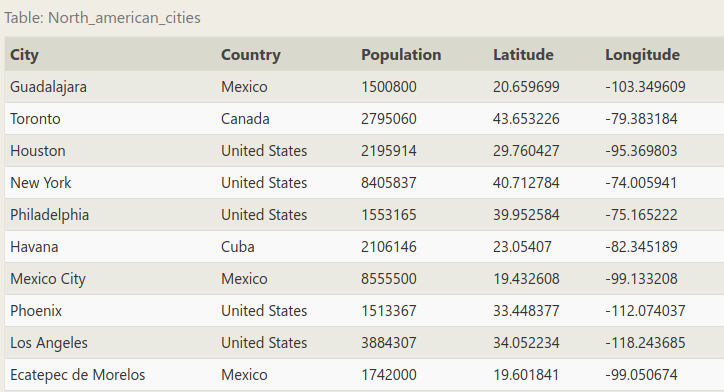
Positive latitudes correspond to the northern hemisphere, and positive longitudes correspond to the eastern hemisphere. Since North America is north of the equator and west of the prime meridian, all of the cities in the list have positive latitudes and negative longitudes.
经度和纬度的正值表示东经和北纬。由于北美在西、北半球,所以表格里的城市都是负经度和正纬度的。
Try and write some queries to find the information requested in the tasks you know. You may have to use a different combination of clauses in your query for each task. Once you’re done, continue onto the next lesson to learn about queries that span multiple tables.
这次的练习需要组合使用前面学过的东西了。有点小紧张呢,来吧。
1. List all the Canadian cities and their populations
所有 Canada 城市及其人口,
|
|
2. Order all the cities in the United States by their latitude from north to south
美国城市按纬度从北到南,由于北美纬度都是正值,北到南那就是从大到小即降序咯,
|
|
3. List all the cities west of Chicago, ordered from west to east
Chicago 以西的城市从西到东排。经度全是负值,越往西负值越大(负数越小),那就是比 Chicago 经度更小的从小往大排(升序)咯,
|
|
Chicago 的经度得自己手动查询输入,想起了高中考试不给原子质量表和分子质量表得自己死记,差评。
4. List the two largest cities in Mexico (by population)
Mexico 人口最大的两个城市,
|
|
5. List the third and fourth largest cities (by population) in the United States and their population
美国第 3、4 大人口市,嗯,考点 OFFSET,
|
|
1 - 5 课上完,大部分东西之前接触过,还比较轻松。这一篇先写到这里吧。
文章作者 Jackie
上次更新 2019-01-06 (b1fedc7)